The global supply chain is undergoing a dramatic transformation, and at the heart of this revolution lies blockchain technology. This groundbreaking innovation is poised to reshape supply chain management (SCM) by enhancing transparency, security, and efficiency. This article will explore five key ways blockchain is revolutionizing SCM, impacting everything from product traceability and fraud prevention to improved logistics and enhanced collaboration among stakeholders. Learn how this cutting-edge technology is streamlining processes, boosting trust, and ultimately creating a more resilient and robust global supply chain.
Enhancing Transparency with Immutable Records
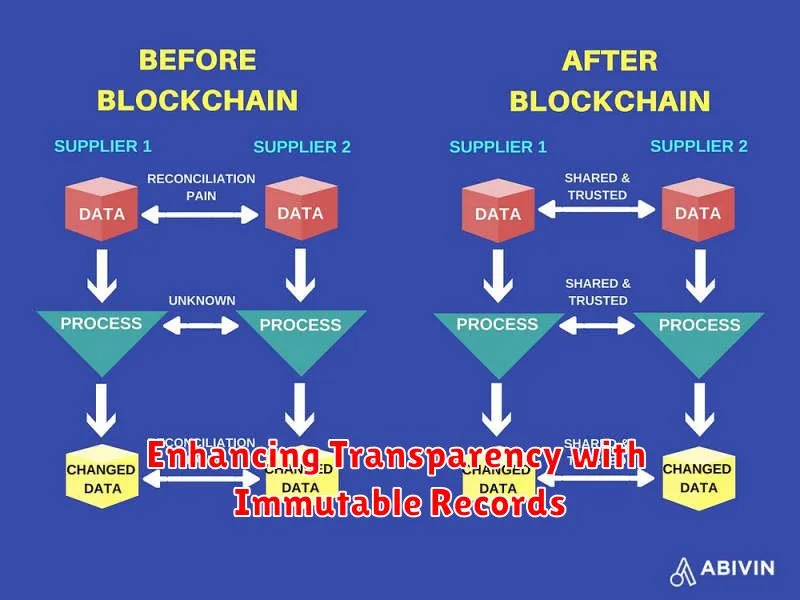
The concept of immutable records offers a powerful solution for enhancing transparency and trust in various systems. By ensuring that data, once recorded, cannot be altered or deleted, immutability provides a robust audit trail, fostering accountability and preventing fraudulent activities.
Data integrity is significantly improved with immutable records. The inherent resistance to tampering guarantees that the information remains accurate and reliable, eliminating concerns about data manipulation or accidental modifications. This is particularly crucial in applications requiring high levels of data accuracy, such as financial transactions or legal documentation.
Enhanced security is another key benefit. The inability to alter past records strengthens the system’s defense against cyberattacks and data breaches. Even if unauthorized access occurs, the integrity of the historical data remains intact, minimizing the impact of the breach and simplifying forensic analysis.
Improved traceability is facilitated by immutable records. Every change or action is permanently recorded, creating a comprehensive and verifiable history. This allows for thorough investigations, simplifies troubleshooting, and improves the overall understanding of system behavior.
Implementing immutable records requires careful consideration of storage and management strategies. Solutions often involve technologies like blockchain, cryptographic hashing, and distributed ledger systems. The choice of technology depends on the specific requirements of the application and the desired level of security and scalability.
In conclusion, immutable records represent a significant advancement in data management, providing unparalleled transparency, security, and traceability. By preventing alterations and ensuring data integrity, they foster trust and accountability, ultimately benefiting both organizations and their stakeholders.
Reducing Fraud in Supply Chain Logistics
Supply chain fraud poses a significant threat to businesses of all sizes, impacting profitability, reputation, and even survival. The complexity and global reach of modern supply chains create numerous vulnerabilities that malicious actors exploit.
Implementing robust fraud prevention strategies is crucial. This involves a multi-faceted approach encompassing technological solutions and rigorous internal controls. Technology plays a vital role, with solutions like blockchain technology offering enhanced transparency and traceability, making it significantly harder to manipulate data or divert goods.
Data analytics is another powerful tool. Analyzing large datasets can reveal anomalies and patterns indicative of fraudulent activity, allowing for proactive intervention. Machine learning algorithms can identify high-risk transactions and flag them for further investigation, significantly improving detection rates.
Beyond technology, strong internal controls are essential. This includes thorough background checks on suppliers and partners, clear segregation of duties, regular audits, and a robust system for reporting and investigating suspected fraud. Employee training is also critical, equipping staff with the knowledge to identify and report suspicious activities.
Effective risk assessment is paramount. Identifying potential vulnerabilities within the supply chain allows for the implementation of targeted preventative measures. Regularly reviewing and updating this assessment is crucial, as risks can evolve over time.
Finally, fostering a culture of compliance and ethics is vital. Employees should be empowered to report suspicious activity without fear of retribution. A strong ethical foundation throughout the organization significantly reduces the likelihood of fraudulent behavior.
By combining technological advancements with robust internal controls and a strong ethical culture, organizations can significantly reduce their vulnerability to supply chain fraud, safeguarding their assets and protecting their reputation.
Smart Contracts for Automated Transactions
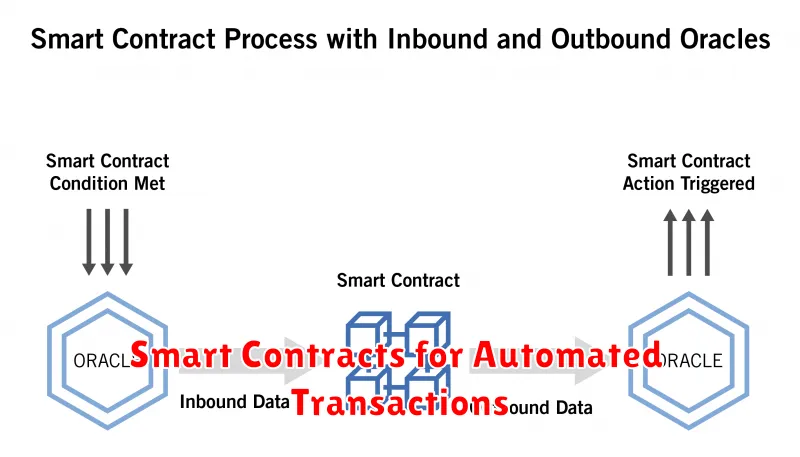
Smart contracts represent a groundbreaking innovation in the realm of automated transactions. These self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code are transforming how we conduct business across various sectors.
Their core functionality lies in their ability to automate the execution of agreements. Once predefined conditions are met, the contract automatically performs the stipulated actions without the need for intermediaries. This eliminates inefficiencies, reduces costs, and enhances transparency.
The decentralized nature of many smart contract platforms, often leveraging blockchain technology, ensures immutability and security. This means that once a contract is deployed, it cannot be altered or tampered with, fostering trust among parties involved.
Applications of smart contracts are vast and diverse, spanning supply chain management, escrow services, digital identity verification, and decentralized finance (DeFi). Their potential to streamline complex processes and reduce reliance on trust-based intermediaries is significant.
However, it is crucial to acknowledge the challenges associated with smart contracts. Developing secure and robust code requires significant expertise to prevent vulnerabilities and ensure the contract functions as intended. Legal and regulatory frameworks are still evolving to address the unique aspects of smart contract agreements.
Despite these challenges, the future of smart contracts appears bright. Ongoing advancements in technology and the increasing understanding of their potential are driving widespread adoption across numerous industries. As the technology matures and regulatory clarity emerges, smart contracts are poised to fundamentally reshape how transactions are conducted globally.
Tracking Goods in Real-Time
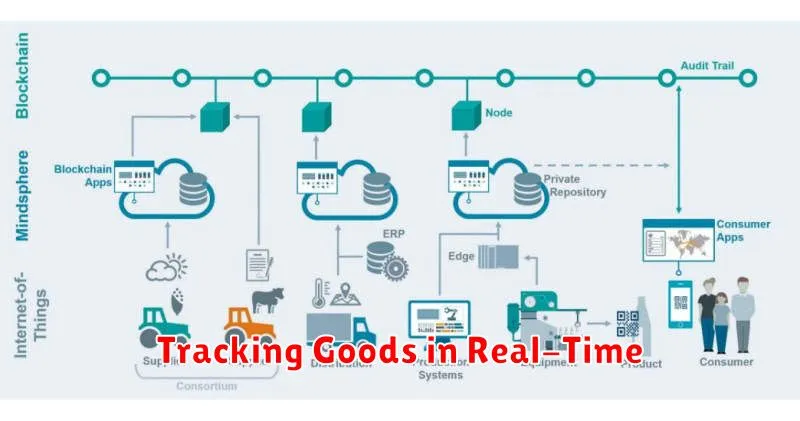
Real-time tracking of goods has become increasingly crucial in today’s fast-paced global supply chains. Accuracy and speed are paramount, impacting everything from customer satisfaction to operational efficiency.
Real-time tracking systems leverage various technologies, including GPS, RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification), and IoT (Internet of Things) sensors. These technologies provide continuous updates on a good’s location, condition, and handling, enabling businesses to monitor shipments at every stage of the journey.
The benefits are significant. Businesses gain improved visibility into their supply chain, allowing for proactive management of potential disruptions. Predictive analytics, powered by real-time data, can help anticipate delays and optimize logistics. This leads to reduced costs associated with delays, improved inventory management, and enhanced customer service through precise delivery estimations.
Data security is a primary concern when implementing real-time tracking. Robust security measures are essential to protect sensitive information related to goods and their movement. Choosing a reputable provider with strong security protocols is vital for minimizing risks.
While the initial investment in real-time tracking technology can be substantial, the long-term return on investment (ROI) is often considerable. The improved efficiency, reduced losses, and enhanced customer satisfaction far outweigh the initial costs for many businesses.
The future of goods tracking is likely to involve even more sophisticated technologies, such as AI and blockchain, enabling even greater levels of automation, transparency, and security. The continued evolution of these technologies will further refine real-time tracking capabilities, making it an indispensable tool for businesses of all sizes.
Cost Savings and Efficiency Improvements

Implementing new technologies and processes can lead to significant cost savings within an organization. Automation, for example, can reduce labor costs by handling repetitive tasks more efficiently and with fewer errors.
Improved efficiency is another key benefit. Streamlined workflows and optimized processes result in faster turnaround times and increased productivity. This translates to reduced operational expenses and a greater return on investment (ROI).
Analyzing data analytics can reveal areas for improvement that might otherwise go unnoticed. By identifying bottlenecks and inefficiencies, businesses can make targeted changes to optimize their operations and reduce waste.
The adoption of cloud-based solutions can also contribute to substantial cost savings. Reduced infrastructure costs, scalability, and easier maintenance are just some of the advantages. This allows businesses to allocate resources more effectively and focus on core competencies.
Ultimately, the pursuit of cost savings and efficiency improvements should be a continuous process. Regularly reviewing operations and exploring new technologies will help organizations stay competitive and maintain a healthy bottom line.
